CS336 Assignment 1#
Part1中我们实现了BPE分词器的算法以及Tokenizer类, 在Part2中我们将会手搓整个Transformer模型, 然后在Part3中我们会把前面的部分结合来真正的让这个模型开始训练
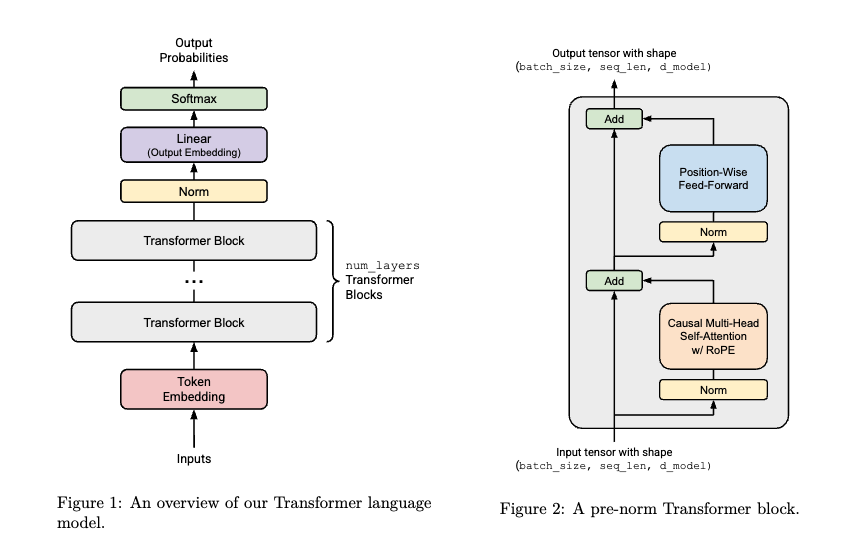
Transformer LM 简介#
Token嵌入层 (Token Embedding)#
输入Transformer的内容是token id数字张量(显然不能是char), 形状为(batch_size, sequence_length), 比如说(2,2)
inputs = np.array([[2,0],[1,2]]) 然后有一个可训练的矩阵E称之为嵌入矩阵, 这个矩阵回答这样一个问题: 对于每个输入的token_id(一维数字), 怎么把他送到高维空间?
该矩阵形如:
E = np.array([
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0], # id = 0 (PAD/UNK)
[0.1, 0.2, 0.3], # id = 1 Somewhere
[0.0, 0.5, 0.5], # id = 2 over
[0.9, 0.1, 0.0], # id = 3 the
[0.4, 0.4, 0.2], # id = 4 rainbow
[0.7, 0.3, 0.6], # id = 5 way
[0.2, 0.2, 0.9], # id = 6 up
[0.6, 0.1, 0.4], # id = 7 high
]) # shape (V, d_model) -> here V=8, d_model=3含义为: 将输入的token_id当中的0送到上, 值为[0.1,0.2,0.3], 至于这些token_id是哪里来的, 就是从之前训练好的Vocab训练而来的, 完整的流程如下
这是我们输入的自然语言:
Somewhere over the rainbow way up high.我们有训练好的词汇表Vocab:
{"Somewhere":1, "over",2, "the":3, "rainbow":4, "way":5, "up":6, "high":7}首先自然语言被分割成
tokens = ["Somewhere","over","the","rainbow","way","up","high"]然后通过词汇表被编码成
ids = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]接着对于ids里面的每一个id, 直接在E里面找到对应的行就可以了, 这就完成了Token Embeddings这个步骤
Pre-Norm Transformer块#
经过Embedding处理后的尺寸为(batch_size, sequence_length, d_model)的数据被送入Pre-Norm Transformer块当中, 处理完毕后的尺寸仍为(batch_size, sequence_length, d_model), 块内的组件是自注意力机制和前馈层
输出的归一化#
在经过若干个Transformer块之后, 还要进行归一化, 再送入一个线性层做处理, 最后通过Softmax来输出概率logits来决定下一个词输出什么
Einstein算子标注#
显然在做矩阵乘法/张量乘法的时候, 我们是在某一个维度进行求和, 而那个维度在计算完成之后会消失, Einstein算子标注就是让我们显性的写出那个被求和/将消失的维度, 其他的维度就不管了
我觉得这种张亮乘法其实类似于高维定积分, 当通过累次积分来计算重积分的时候, 显然要写好这一次是对什么变量进行积分, 这次积分完毕之后, 这个变量就不再存在
后面那次积分的dz已经说明了这次的积分(视作特殊的求和)是对z这个变量的, 所以不会产生混淆
来看一个Einstein标注的张量运算
import torch
from einops import rearrange, einsum
## Basic implementation
Y = D @ A.T
# Hard to tell the input and output shapes and what they mean.
# What shapes can D and A have, and do any of these have unexpected behavior?
## Einsum is self-documenting and robust
# D A -> Y
Y = einsum(D, A, "batch sequence d_in, d_out d_in -> batch sequence d_out")
## Or, a batched version where D can have any leading dimensions but A is constrained.
Y = einsum(D, A, "... d_in, d_out d_in -> ... d_out")这里我们对d_in这个维度求和, 求和后这个维度就消失掉了, 所以只需要在两个运算量里面都亮明这个维度, 算子就会自动求和
再看一个例子
images = torch.randn(64, 128, 128, 3) # (batch, height, width, channel)
dim_by = torch.linspace(start=0.0, end=1.0, steps=10)
## Reshape and multiply
dim_value = rearrange(dim_by, "dim_value -> 1 dim_value 1 1 1") # 拓展维度, 注意1是可以任意添加的维度
images_rearr = rearrange(images, "b height width channel -> b 1 height width channel") # 同上
dimmed_images = images_rearr * dim_value
## Or in one go:
dimmed_images = einsum(
images, dim_by,
"batch height width channel, dim_value -> batch dim_value height width channel"
)注意一下广播的时候首先维度的数量要匹配, 其次每个维度的大小要么相等要么有一个是1, 而在Einstein标注下, 不足的维度会被自动填充并广播
高维张量的乘法是不便想象的, 我觉得首先要明白需要的输出尺寸是多少, 然后再用Einstein标注去写好输入的尺寸, 不变的用...替代
线性变换标注#
本项目中统一使用列向量做线性变换的notation, 即若对向量x进行线性变换W则:
x默认为列向量
线性层和嵌入模块#
参数初始化#
对于每一个权重矩阵, 需要把它声明为nn.Parameter参数并且传入shape, 然后对这个参数做初始化, 比如在线性层当中想构造一个out_features * in_features的权重矩阵并且正态初始化
weight = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(out_features, in_features))
nn.init.trunc_normal_(weight,mean = mean, std = std, a = -3*std, b = 3*std)对于不同的层, 文档给了我们不同的初始化要求
所有的参数初始化都用torch.nn.init.trunc_normal_来实现
线性层#
很容易实现, 就是声明并初始化一个权重矩阵并且作用在输入上面就可以了
# transformer.py
class Linear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_features,out_features,device=None,dtype=None):
super().__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.device = device
self.dtype = dtype
std = 2/(self.in_features+self.out_features)
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(self.out_features, self.in_features))
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.weight, mean=0, std=std, a=-3*std, b=3*std)
def forward(self,x:torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return torch.einsum("ji,...i->...j",self.weight,x)很常规, 解释一下最后这个einsum的notation, 先忽略这个..., 就看"ji,i->j"
从逐行求和的角度看, 结果的第j行满足
所以是对i这个维度求和, 求和的维度会消失, 所以得到输出维度是j
另一种角度看, 消失的总是内在匹配的维度, 所以是这里的i, 即第一个输入的列, 第二个输入的行
完善一下adapters.py里面的测试, 直接调用自己实现的这个Linear类就好了, 注意对于那些权重矩阵, 记得更新他们的内容, 后面所有的测试都是这个格式, 依葫芦画瓢就好了
# adapters.py
from cs336_basics import transformer
def run_linear(
d_in: int,
d_out: int,
weights: Float[Tensor, " d_out d_in"],
in_features: Float[Tensor, " ... d_in"],
) -> Float[Tensor, " ... d_out"]:
"""
Given the weights of a Linear layer, compute the transformation of a batched input.
Args:
in_dim (int): The size of the input dimension
out_dim (int): The size of the output dimension
weights (Float[Tensor, "d_out d_in"]): The linear weights to use
in_features (Float[Tensor, "... d_in"]): The output tensor to apply the function to
Returns:
Float[Tensor, "... d_out"]: The transformed output of your linear module.
"""
# raise NotImplementedError
linear_module = transformer.Linear(in_features=d_in,out_features=d_out)
linear_module.weight.data = weights
return linear_module(in_features)运行测试uv run pytest -k test_linear, 结果如下:
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_linear
==================================================================================================== test session starts =====================================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 47 deselected / 1 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_linear PASSED
============================================================================================== 1 passed, 47 deselected in 0.19s ==============================================================================================嵌入模块#
和我们之前讲的一样, 这里就是把输入的token_id在Embedding矩阵当中去寻找相应的d_model维度的向量, 也就是一个升维的过程, 比如说输入为5, 那就去找Embedding矩阵的第五行的行向量就好了
# transformer.py
class Embedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,num_embeddings,embedding_dim,device=None,dtype=None):
super().__init__()
self.num_embeddings = num_embeddings
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.device = device
self.dtype = dtype
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(self.num_embeddings, self.embedding_dim))
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.weight, mean=0, std=1, a=-3, b=3)
def forward(self,token_ids:torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return self.weight[token_ids]注意self.weight[token_ids]这种写法, 实际上nn.Parameter是tensor的子类, 是可以通过索引访问的, 举个例子
# weight: (num_embeddings=5, embedding_dim=3)
weight = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor([
[0.1, 0.2, 0.3], # id 0
[0.4, 0.5, 0.6], # id 1
[0.7, 0.8, 0.9], # id 2
[1.0, 1.1, 1.2], # id 3
[1.3, 1.4, 1.5], # id 4
], dtype=torch.float32))
token_ids = torch.tensor([[2,0],
[1,2]], dtype=torch.long) # shape (2,2)
# 索引取 embedding:结果形状 (2, 2, 3)
embs = weight[token_ids]输出类似于
tensor([
[[0.7, 0.8, 0.9], # weight[2]
[0.1, 0.2, 0.3]], # weight[0]
[[0.4, 0.5, 0.6], # weight[1]
[0.7, 0.8, 0.9]] # weight[2]
])不过也不需要了解, 反正知道支持下标访问就行了, 而且这个下标还可以是一个tensor
# adapters.py
def run_embedding(
vocab_size: int,
d_model: int,
weights: Float[Tensor, " vocab_size d_model"],
token_ids: Int[Tensor, " ..."],
) -> Float[Tensor, " ... d_model"]:
"""
Given the weights of an Embedding layer, get the embeddings for a batch of token ids.
Args:
vocab_size (int): The number of embeddings in the vocabulary
d_model (int): The size of the embedding dimension
weights (Float[Tensor, "vocab_size d_model"]): The embedding vectors to fetch from
token_ids (Int[Tensor, "..."]): The set of token ids to fetch from the Embedding layer
Returns:
Float[Tensor, "... d_model"]: Batch of embeddings returned by your Embedding layer.
"""
# raise NotImplementedError
embedding_module = transformer.Embedding(num_embeddings=vocab_size,embedding_dim=d_model)
embedding_module.weight.data = weights
return embedding_module(token_ids)运行测试uv run pytest -k test_embedding, 结果如下:
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_embedding
==================================================================================================== test session starts =====================================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 47 deselected / 1 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_embedding PASSED
============================================================================================== 1 passed, 47 deselected in 0.21s ==============================================================================================Pre-Norm Transformer块#
这里主要需要实现三个模块, RMSNorm归一化, RoPE旋转编码, Feed-Forward前馈神经网络
RMSNorm---Root Mean Square Layer Normalization 均方根归一化#
对于向量, RMSNorm会对每个分量a_i进行如下变化:
其中是一个平方根式求和
很好理解, 这个分母真的就是均值->平方求和->开根号(忽略那个)
是一个可学习的向量, 注意每个有一个, 总共有个, 所以有个
# transformer.py
class rmsnorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,d_model:int,eps:float=1e-5,device=None,dtype=None):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.eps = eps
self.device = device
self.dtype = dtype
self.weights = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(self.d_model))
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.weights, mean=0, std=1, a=-3, b=3)
def forward(self,x:torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
in_dtype = x.dtype
x = x.to(torch.float32)
RMS_a = torch.sqrt(torch.einsum("...d,...d->...",x,x)/self.d_model + self.eps)
return ((x/RMS_a.unsqueeze(-1))*self.weights).to(in_dtype)解释一下这个RMS_a的算法当中的einsum部分, 实际上这里是要算内积分, 所以对于两个一模一样的东西, 直接按照最后一个维度求和就好了
注意这里这个RMS_a.unsqueeze(-1)是不可以省略的, 因为RMS_a的尺寸是..., 而x的尺寸是...d, 所以必须给RMS_a的尺寸做成...1才能进行除法的广播, 实际上这个RMS_a是个标量, 广播的意思就是每个都要去除以这个标量, 这就必须要求最后一个维度是对齐的, 不然广播会出错
# adapters.py
def run_rmsnorm(
d_model: int,
eps: float,
weights: Float[Tensor, " d_model"],
in_features: Float[Tensor, " ... d_model"],
) -> Float[Tensor, " ... d_model"]:
"""Given the weights of a RMSNorm affine transform,
return the output of running RMSNorm on the input features.
Args:
d_model (int): The dimensionality of the RMSNorm input.
eps: (float): A value added to the denominator for numerical stability.
weights (Float[Tensor, "d_model"]): RMSNorm weights.
in_features (Float[Tensor, "... d_model"]): Input features to run RMSNorm on. Can have arbitrary leading
dimensions.
Returns:
Float[Tensor,"... d_model"]: Tensor of with the same shape as `in_features` with the output of running
RMSNorm of the `in_features`.
"""
# raise NotImplementedError
rmsnorm_module = transformer.rmsnorm(d_model=d_model,eps=eps)
rmsnorm_module.weights.data = weights
return rmsnorm_module(in_features)运行测试uv run pytest -k test_rmsnorm, 结果如下:
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_rmsnorm
==================================================================================================== test session starts =====================================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 47 deselected / 1 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_rmsnorm PASSED
============================================================================================== 1 passed, 47 deselected in 0.18s ==============================================================================================前馈神经网络#
虽然说是神经网络, 但是其实就是设计一个激活函数, 大概用的有以下几种:
SiLU/Swish
Gated Linear Units/GLU
该算子为Hadamard积, 即逐元素相乘
SwiGLU
考虑一下SwiGLU的尺寸问题, 输入的x是(...,d_model), 经过SwiGLU的变换之后仍然应该是这个尺寸, 所以W_1和W_3的尺寸应当是(d_ff, d_model), W_2应该是(d_model, d_ff)
借用torch.sigmoid实现这个SwiGLU的代码:
# transformer.py
class positionwise_feedforward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,d_model,d_ff):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.d_ff = d_ff
self.w1_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(self.d_ff, self.d_model))
self.w2_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(self.d_model, self.d_ff))
self.w3_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(self.d_ff, self.d_model))
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.w1_weight, mean=0, std=1, a=-3, b=3)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.w2_weight, mean=0, std=1, a=-3, b=3)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.w3_weight, mean=0, std=1, a=-3, b=3)
def silu(self,x):
return torch.sigmoid(x) * x
def element_wise(self,x,y):
return torch.einsum("...,...->...",x,y)
def forward(self,x):
w3x = torch.einsum("...d,fd->...f",x ,self.w3_weight)
w1x = torch.einsum("...d,fd->...f",x ,self.w1_weight)
silu_w1x = self.silu(w1x)
swiglu_ouptut = self.element_wise(silu_w1x,w3x)
output = torch.einsum("...f,df->...d", swiglu_ouptut, self.w2_weight)
return output还是讲一下这里的维度notation, 首先对于Hadamard算子应该是比较好理解的, 前后尺寸都是...,意味着不对任何维度求和, 那当然就是逐元素相乘
对于W_3x而言, 这里写的看起来像是xW_3, 不过关键还是要对齐那个可以匹配的维度, 由于x是(...,d_model), W_3是(d_ff, d_model), 显然写的时候要确保最后一维的尺寸一致(即d), 然后对这个维度求和(即不出现在结果里面就好了)
在工程上或许这么写不会有什么问题, 毕竟这块以后都会封装, 也没有谁真的会去看, 不过如果是数学作业/paper上还是保持notation的顺序比较好, 不然读者的脸色可能不会太好看
# adapters.py
def run_swiglu(
d_model: int,
d_ff: int,
w1_weight: Float[Tensor, " d_ff d_model"],
w2_weight: Float[Tensor, " d_model d_ff"],
w3_weight: Float[Tensor, " d_ff d_model"],
in_features: Float[Tensor, " ... d_model"],
) -> Float[Tensor, " ... d_model"]:
"""Given the weights of a SwiGLU network, return
the output of your implementation with these weights.
Args:
d_model (int): Dimensionality of the feedforward input and output.
d_ff (int): Dimensionality of the up-project happening internally to your swiglu.
w1_weight (Float[Tensor, "d_ff d_model"]): Stored weights for W1
w2_weight (Float[Tensor, "d_model d_ff"]): Stored weights for W2
w3_weight (Float[Tensor, "d_ff d_model"]): Stored weights for W3
in_features (Float[Tensor, "... d_model"]): Input embeddings to the feed-forward layer.
Returns:
Float[Tensor, "... d_model"]: Output embeddings of the same shape as the input embeddings.
"""
# raise NotImplementedError
swiglu_module = transformer.positionwise_feedforward(d_ff=d_ff,d_model=d_model)
swiglu_module.w1_weight.data = w1_weight
swiglu_module.w2_weight.data = w2_weight
swiglu_module.w3_weight.data = w3_weight
return swiglu_module(in_features)运行测试uv run pytest -k test_swiglu, 结果如下:
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_swiglu
Uninstalled 1 package in 0.92ms
Installed 1 package in 16ms
================================================================================================= test session starts ==================================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 47 deselected / 1 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_swiglu PASSED
=========================================================================================== 1 passed, 47 deselected in 0.18s ===========================================================================================相对位置编码#
相对位置编码和多头注意力机制应该是最难的, 先不考虑代码的问题, 我们先来理解一下这玩意到底是在干什么
首先RoPE接受一个参数, 这会决定我们每次旋转的角度
两个index:i和k, i代表的是输入的索引, 也就是这是输入的第几条输出, k代表的是现在是在对这个输出的第几组维度进行变换, 对于每一组(i, k), 变换的角度, 其中d指的是d_model, 为固定的模型参数
维度是被两两分组的, 比如说d_model是8, 那就被切分成4组,
每一组的旋转矩阵为:
现在对来做变换, 的i=1, k被分为两组, 1和2, 那么可以计算出以下两个
进而得到两个旋转矩阵, 那么组一是, , 分别对其左乘即可
写成比较大的矩阵形式就是:
那么整个的RoPE就是, 一句话总结就是先把分组, 然后每组构造一个2*2的旋转矩阵, 对每个组左乘这个旋转矩阵之后凑起来就得到了RoPE的结果
实验文档中提出了用self.register_buffer来注册这些三角函数值, 因为他们只依赖于输入角度theta, 输入的”编号”i以及离散取值于的k, 所以可以在初始化的时候就把他们确定下来
注意, 他的指标应该是i和k的笛卡尔积, 这样才能保证每个i和k都能被遍历到, 所以应当通过以下代码来建立这个
positions = torch.arange(sequence_length).float() # i的向量
freqs = theta ** (torch.arange(0, self.d_k , 2).float() / self.d_k) # theta^{2k-2/d}的向量
angles = torch.outer(positions, freqs) # i和K的笛卡尔积然后注册成为类buffer
self.register_buffer("cos_cached", torch.cos(angles), persistent = False)
self.register_buffer("sin_cached", torch.sin(angles), persistent = False)如此一来的话就可以通过token_positions来访问得到和了, 例如:
cos_pos = self.cos_cached[token_positions] # 直接拿到这个x所需的所有cos值, 注意token_positions是个tensor
sin_pos = self.sin_cached[token_positions]回想一下在之前的变换矩阵示意图里面, 这个变换最后并不改变输入x的shape, 但是要能把这个分块d/2 * d/2的变换矩阵作用上去, 是需要对x进行一些reshape的
x_reshaped = x.view(batch_size,seq_len,d_k//2,2) # 分成d_k//2个组, 每组两个元素
x1,x2 = x_reshaped[...,0],x_reshaped[...,1] # 对于每个组, 把第一个元素和第二个元素分开然后进行变换并且stack回去即可
x1_rotated = x1 * cos_pos - x2 * sin_pos # 注意这里的x_1是: "一个输入token(一个i)"的所有的d_k//2个组的x_1, 不只是一个组的x_1
x2_rotated = x2 * cos_pos + x1 * sin_pos
# 如果说输入的x = [1,2,3,4,5,6], 那么这里的x_1是形如[1,3,5]的tensor, 所以这个变换是向量化的
x_rotated = torch.stack([x1_rotated, x2_rotated], dim=-1)
x_rotated = x_rotated.view(batch_size, seq_len, d_k)整体代码如下:
# transformer.py
class RoPE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,theta,d_k,max_seq_len,device=None):
super().__init__()
self.theta = theta
self.d_k = d_k
self.max_seq_len = max_seq_len
self.device = device
freqs = self.theta ** (torch.arange(0,self.d_k,2).float()/d_k)
positions = torch.arange(max_seq_len).float()
angles = torch.outer(positions,1.0/freqs)
self.register_buffer("cos_cached", torch.cos(angles),persistent=False)
self.register_buffer("sin_cached", torch.sin(angles),persistent=False)
def forward(self,x:torch.Tensor,token_positions:torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
batch_size,seq_len,d_k = x.shape
cos_pos = self.cos_cached[token_positions]
sin_pos = self.sin_cached[token_positions]
x_reshaped = x.view(batch_size,seq_len,d_k//2,2)
x1,x2 = x_reshaped[...,0],x_reshaped[...,1]
x1_rotated = x1 * cos_pos - x2 * sin_pos
x2_rotated = x2 * cos_pos + x1 * sin_pos
x_rotated = torch.stack([x1_rotated, x2_rotated], dim=-1)
x_rotated = x_rotated.view(batch_size, seq_len, d_k)
return x_rotated完善测试:
# adapters.py
def run_rope(
d_k: int,
theta: float,
max_seq_len: int,
in_query_or_key: Float[Tensor, " ... sequence_length d_k"],
token_positions: Int[Tensor, " ... sequence_length"],
) -> Float[Tensor, " ... sequence_length d_k"]:
"""
Run RoPE for a given input tensor.
Args:
d_k (int): Embedding dimension size for the query or key tensor.
theta (float): RoPE parameter.
max_seq_len (int): Maximum sequence length to pre-cache if your implementation does that.
in_query_or_key (Float[Tensor, "... sequence_length d_k"]): Input tensor to run RoPE on.
token_positions (Int[Tensor, "... sequence_length"]): Tensor of shape (batch_size, sequence_length) with the token positions
Returns:
Float[Tensor, " ... sequence_length d_k"]: Tensor with RoPEd input.
"""
# raise NotImplementedError
RoPE = transformer.RoPE(theta=theta,d_k=d_k,max_seq_len=max_seq_len)
return RoPE(in_query_or_key,token_positions)运行测试uv run pytest -k test_rope, 结果如下:
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_rope
========================================================================================== test session starts ==========================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 47 deselected / 1 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_rope PASSED
=================================================================================== 1 passed, 47 deselected in 0.17s ====================================================================================Softmax和点积注意力机制#
首先实现Softmax函数, 对向量做归一化
注意求指数有可能会让数据变得很大从而上溢出, 所以一个比较好的办法是让这个向量的每个分量减去这个向量的最大分量, 因为对一个很小的数求指数是不会溢出的
# transformer.py
class Softmax(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, x:torch.Tensor, dimension:int):
super().__init__()
self.x = x
self.dimension = dimension
def forward(self):
x_shifted = self.x - torch.max(self.x,dim = self.dimension,keepdim=True)[0]
exp_x = torch.exp(x_shifted)
sum_exp_x = torch.sum(exp_x, dim=self.dimension, keepdim=True)
return exp_x / sum_exp_x完善测试:
# adapters.py
def run_softmax(in_features: Float[Tensor, " ..."], dim: int) -> Float[Tensor, " ..."]:
"""
Given a tensor of inputs, return the output of softmaxing the given `dim`
of the input.
Args:
in_features (Float[Tensor, "..."]): Input features to softmax. Shape is arbitrary.
dim (int): Dimension of the `in_features` to apply softmax to.
Returns:
Float[Tensor, "..."]: Tensor of with the same shape as `in_features` with the output of
softmax normalizing the specified `dim`.
"""
# raise NotImplementedError
softmax_module = transformer.Softmax(in_features,dim)
return softmax_module()注意这个dim是必须的参数, 因为需要知道对什么维度进行归一化
运行测试uv run pytest -k test_softmax_matches_pytorch, 结果如下:
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_softmax_matches_pytorch
========================================================================================== test session starts ==========================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 47 deselected / 1 selected
tests/test_nn_utils.py::test_softmax_matches_pytorch PASSED
=================================================================================== 1 passed, 47 deselected in 0.17s ====================================================================================接下来计算点积注意力
先考虑一下尺寸问题, 简单来说, 假设, , , 那么输出尺寸应该是, 但是如果按照一般的矩阵乘法是不能相乘的, 这里其实对这两个矩阵的每个行向量做内积
注意求和, 每行有个元素, 实验文档要求我们用einsum来实现这个求和, 如果是用pytorch的话, 这里要手动修改成的乘积形式
但我觉得这种记号并不好, 既然用了矩阵乘法的记号, 那应该要确保按照记号是可相乘的, 不然当发现维度不匹配的时候会很confused
scores = torch.einsum("b...qd,b...kd->b...qk",self.Q,self.K)/torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(self.d_k,dtype=torch.float32))
# kd 指的是Q当中的n * d_k
# qd 指的是K当中的m * d_k
# 匹配的是最后一维, einsum会自动把他们转置成可以相乘的形式然后用mask做掩码变换, 这里mask的维度是, 暂时不需要管他怎么实现的, 当作类里有的成员变量就好, 既然他是个布尔矩阵, 那只要用torch.where去把mask和计算出的分数做一个类似与运算就好了
if self.mask is not None:
scores = torch.where(self.mask,scores,float('-inf'))接下来做Softmax变换, 对最后一维做归一化
attention_weights = torch.softmax(scores, dim=-1)最后乘以即可, 注意前面的结果是可以”直接”乘以的, 因为维度已经匹配了, 而像之前那样维度不匹配的情况, einsum会自动把他们转置成可以相乘的形式
output = torch.einsum("b...qk,b...kv->b...qv",attention_weights,self.V)
return output总体实现如下
# transformer.py
class scaled_dot_product_attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,K,Q,V,mask):
super().__init__()
self.Q = Q # [batch,...seq_q,d_q]
self.K = K # [batch,...,seq_k,d_k]
self.V = V # [batch,...,seq_k,d_v]
self.mask = mask # [seq_q,seq_k]
self.d_k = Q.shape[-1]
def forward(self):
scores = torch.einsum("b...qd,b...kd->b...qk",self.Q,self.K)/torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(self.d_k,dtype=torch.float32))
if self.mask is not None:
scores = torch.where(self.mask,scores,float('-inf'))
attention_weights = torch.softmax(scores, dim=-1)
output = torch.einsum("b...qk,b...kv->b...qv",attention_weights,self.V)
return output完善测试:
# adapters.py
def run_scaled_dot_product_attention(
Q: Float[Tensor, " ... queries d_k"],
K: Float[Tensor, " ... keys d_k"],
V: Float[Tensor, " ... values d_v"],
mask: Bool[Tensor, " ... queries keys"] | None = None,
) -> Float[Tensor, " ... queries d_v"]:
"""
Given key (K), query (Q), and value (V) tensors, return
the output of your scaled dot product attention implementation.
Args:
Q (Float[Tensor, " ... queries d_k"]): Query tensor
K (Float[Tensor, " ... keys d_k"]): Key tensor
V (Float[Tensor, " ... values d_v"]): Values tensor
mask (Bool[Tensor, " ... queries keys"] | None): Mask tensor
Returns:
Float[Tensor, " ... queries d_v"]: Output of SDPA
"""
# raise NotImplementedError
attention = transformer.scaled_dot_product_attention(K,Q,V,mask)
return attention()这里有两个测试, 分别运行uv run pytest -k test_scaled_dot_product_attention和uv run pytest -k test_4d_scaled_dot_product_attention, 结果如下
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_scaled_dot_product_attention
========================================================================================== test session starts ==========================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 47 deselected / 1 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_scaled_dot_product_attention PASSED
=================================================================================== 1 passed, 47 deselected in 0.17s ====================================================================================
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_4d_scaled_dot_product_attention
========================================================================================== test session starts ==========================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 47 deselected / 1 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_4d_scaled_dot_product_attention PASSED
=================================================================================== 1 passed, 47 deselected in 0.44s ====================================================================================多头注意力机制#
之前我们只关心怎么通过来计算出注意力, 但是没有探究这个是怎么通过输入x得到的, 实际上我们有以下的流程图
输入 x: (batch, seq_len, d_model)
↓
┌────┴────┐
↓ ↓
WQ x: (batch, seq_len, h×d_k) WK x: (batch, seq_len, h×d_k)
WV x: (batch, seq_len, h×d_v)
↓
按头切分 (split) 总共h个头
↓
Q: (batch, seq_len, h, d_k) → view成 (batch×h, seq_len, d_k)
K: (batch, seq_len, h, d_k) → view成 (batch×h, seq_len, d_k)
V: (batch, seq_len, h, d_v) → view成 (batch×h, seq_len, d_v)
↓
多头注意力计算
↓
输出: (batch×h, seq_len, d_v)
↓
Concat所有头
↓
输出: (batch, seq_len, h×d_v)
↓
WO
↓
最终输出: (batch, seq_len, d_model)也就是说, 先通过三个不同的线性层把输入x变换到三个矩阵, 然后通过多头注意力机制计算出注意力, 最后通过一个线性层把多个头的结果拼接起来, 再通过一个线性层得到最终的输出
self.d_model = d_model
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.q_proj = Linear(d_model, num_heads * self.d_k)
self.k_proj = Linear(d_model, num_heads * self.d_k)
self.v_proj = Linear(d_model, num_heads * self.d_k)
self.output_proj = Linear(num_heads * self.d_v, d_model)
batch_size, seq_len, d_model = x.shape
Q = self.q_proj(x) # [batch, seq, num_heads * d_k]
K = self.k_proj(x) # [batch, seq, num_heads * d_k]
V = self.v_proj(x) # [batch, seq, num_heads * d_k]
# Rearrange to separate heads
Q = rearrange(Q, "b s (h d) -> b h s d", h=self.num_heads)
K = rearrange(K, "b s (h d) -> b h s d", h=self.num_heads)
V = rearrange(V, "b s (h d) -> b h s d", h=self.num_heads)如果要进行旋转位置编码, 注意每个头上都要应用
if self.use_rope:
# 创建 token_positions [seq_len]
token_positions = torch.arange(seq_len, device=x.device)
# token_positions = self.token_positions
# 为每个头应用 RoPE,形状 [batch, num_heads, seq, d_k]
for head in range(self.num_heads):
Q[:, head, :, :] = self.rope(Q[:, head, :, :], token_positions.unsqueeze(0))
K[:, head, :, :] = self.rope(K[:, head, :, :], token_positions.unsqueeze(0))还需要计算掩码矩阵, 首先考虑尺寸, 实际上mask的尺寸和QK^T的尺寸是一样的, 这里有:
Q: (batch, num_heads, seq_len, d_k)
K: (batch, num_heads, seq_len, d_k)所以mask的尺寸应该是(seq_len, seq_len)
再看mask的元素, 行表示query, 列表示key, 第i个query只能看到前i个’key’, 所以这是个下三角矩阵
allow_mask[i][j] = True 表示 query_i 可以 attend to key_j
key_0 key_1 key_2 key_3
───── ───── ───── ─────
query_0 │ ✓ ✗ ✗ ✗ ← 只能看自己及之前
query_1 │ ✓ ✓ ✗ ✗ ← 只能看自己及之前
query_2 │ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✗ ← 只能看自己及之前
query_3 │ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ← 只能看自己及之前# 添加因果掩码
causal_mask = torch.triu(torch.ones(seq_len, seq_len, device=x.device), diagonal=1).bool()
# scaled_dot_product_attention 期望 mask True = 允许,False = 屏蔽
# 但我们的 causal_mask True = 屏蔽,所以需要取反
allow_mask = ~causal_mask
allow_mask = allow_mask.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(1).expand(batch_size, self.num_heads, -1, -1)然后把得到的传入之前实现的点积注意力机制, 注意这里的都是有head这个维度的, 所以返回的结果也是分head的, 要再通过rearrange把他们拼回去
# 使用 scaled_dot_product_attention 类进行计算
# 注意:参考实现使用 (K, Q, V, mask) 的顺序
attn = scaled_dot_product_attention(K, Q, V, allow_mask)
attended_values = attn() # [batch, num_heads, seq, d_k]
# Rearrange back to [batch, seq, num_heads * d_k]
attended_values = rearrange(attended_values, "b h s d -> b s (h d)", h=self.num_heads)
output = self.output_proj(attended_values) # [batch, seq, d_model]
return output整个实现如下:
# transformer.py
class multihead_self_attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, num_heads, use_rope=True,max_seq_len=1024, theta=10000,token_positions=None):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.use_rope = use_rope
self.token_positions = token_positions
self.d_k = d_model // num_heads
self.d_v = self.d_k
self.q_proj = Linear(d_model, num_heads * self.d_k)
self.k_proj = Linear(d_model, num_heads * self.d_k)
self.v_proj = Linear(d_model, num_heads * self.d_k)
self.output_proj = Linear(num_heads * self.d_v, d_model)
if self.use_rope:
self.rope = RoPE(theta=theta, d_k=self.d_k, max_seq_len=max_seq_len)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
batch_size, seq_len, d_model = x.shape
Q = self.q_proj(x) # [batch, seq, num_heads * d_k]
K = self.k_proj(x) # [batch, seq, num_heads * d_k]
V = self.v_proj(x) # [batch, seq, num_heads * d_k]
# Rearrange to separate heads
Q = rearrange(Q, "b s (h d) -> b h s d", h=self.num_heads)
K = rearrange(K, "b s (h d) -> b h s d", h=self.num_heads)
V = rearrange(V, "b s (h d) -> b h s d", h=self.num_heads)
if self.use_rope:
# 创建 token_positions [seq_len]
token_positions = torch.arange(seq_len, device=x.device)
# token_positions = self.token_positions
# 为每个头应用 RoPE,形状 [batch, num_heads, seq, d_k]
for head in range(self.num_heads):
Q[:, head, :, :] = self.rope(Q[:, head, :, :], token_positions.unsqueeze(0))
K[:, head, :, :] = self.rope(K[:, head, :, :], token_positions.unsqueeze(0))
# 添加因果掩码
causal_mask = torch.triu(torch.ones(seq_len, seq_len, device=x.device), diagonal=1).bool()
# scaled_dot_product_attention 期望 mask True = 允许,False = 屏蔽
# 但我们的 causal_mask True = 屏蔽,所以需要取反
allow_mask = ~causal_mask
allow_mask = allow_mask.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(1).expand(batch_size, self.num_heads, -1, -1)
# 使用 scaled_dot_product_attention 类进行计算
# 注意:参考实现使用 (K, Q, V, mask) 的顺序
attn = scaled_dot_product_attention(K, Q, V, allow_mask)
attended_values = attn() # [batch, num_heads, seq, d_k]
# Rearrange back to [batch, seq, num_heads * d_k]
attended_values = rearrange(attended_values, "b h s d -> b s (h d)", h=self.num_heads)
output = self.output_proj(attended_values) # [batch, seq, d_model]
return output完善测试接口:
# adapters.py
def run_multihead_self_attention(
d_model: int,
num_heads: int,
q_proj_weight: Float[Tensor, " d_k d_in"],
k_proj_weight: Float[Tensor, " d_k d_in"],
v_proj_weight: Float[Tensor, " d_v d_in"],
o_proj_weight: Float[Tensor, " d_model d_v"],
in_features: Float[Tensor, " ... sequence_length d_in"],
) -> Float[Tensor, " ... sequence_length d_out"]:
"""
Given the key, query, and value projection weights of a naive unbatched
implementation of multi-head attention, return the output of an optimized batched
implementation. This implementation should handle the key, query, and value projections
for all heads in a single matrix multiply.
This function should not use RoPE.
See section 3.2.2 of Vaswani et al., 2017.
Args:
d_model (int): Dimensionality of the feedforward input and output.
num_heads (int): Number of heads to use in multi-headed attention.
max_seq_len (int): Maximum sequence length to pre-cache if your implementation does that.
q_proj_weight (Float[Tensor, "d_k d_in"]): Weights for the Q projection
k_proj_weight (Float[Tensor, "d_k d_in"]): Weights for the K projection
v_proj_weight (Float[Tensor, "d_k d_in"]): Weights for the V projection
o_proj_weight (Float[Tensor, "d_model d_v"]): Weights for the output projection
in_features (Float[Tensor, "... sequence_length d_in"]): Tensor to run your implementation on.
Returns:
Float[Tensor, " ... sequence_length d_out"]: Tensor with the output of running your optimized, batched multi-headed attention
implementation with the given QKV projection weights and input features.
"""
# raise NotImplementedError
multihead = transformer.multihead_self_attention(d_model=d_model, num_heads=num_heads, use_rope=False)
multihead.q_proj.weight.data = q_proj_weight
multihead.k_proj.weight.data = k_proj_weight
multihead.v_proj.weight.data = v_proj_weight
multihead.output_proj.weight.data = o_proj_weight
return multihead(in_features)运行测试uv run pytest -k test_multihead_self_attention, 结果如下:
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_multihead_self_attention
========================================================================================== test session starts ==========================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 46 deselected / 2 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_multihead_self_attention PASSED
tests/test_model.py::test_multihead_self_attention_with_rope PASSED
=================================================================================== 2 passed, 46 deselected in 0.43s ====================================================================================组装Transformer#
回忆一下架构图里面, 但我们有了Transformer Block Embedding Layer RMSNorm Linear Softmax之后, 我们就可以来拼装完整的Transformer了
单个的Transformer Block#
照着图拼就行了, 不过要注意类似ResNet的结构
# transformer.py
class transformer_block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,d_model,num_heads,d_ff,use_rope=True,max_seq_len=1024,theta=10000):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.d_ff = d_ff
self.norm1 = rmsnorm(d_model = self.d_model)
self.norm2 = rmsnorm(d_model = self.d_model)
self.attn = multihead_self_attention(d_model = self.d_model, num_heads = self.num_heads, max_seq_len=max_seq_len, theta=theta,use_rope=use_rope)
self.ffn = positionwise_feedforward(d_model = self.d_model, d_ff = self.d_ff)
def forward(self,x):
block1_output = x + self.attn(self.norm1(x))
block2_output = block1_output + self.ffn(self.norm2(block1_output))
return block2_output完善测试接口:
# adapters.py
def run_transformer_block(
d_model: int,
num_heads: int,
d_ff: int,
max_seq_len: int,
theta: float,
weights: dict[str, Tensor],
in_features: Float[Tensor, " batch sequence_length d_model"],
) -> Float[Tensor, " batch sequence_length d_model"]:
"""
Given the weights of a pre-norm Transformer block and input features,
return the output of running the Transformer block on the input features.
This function should use RoPE.
Depending on your implementation, you may simply need to pass the relevant args
to your TransformerBlock constructor, or you may need to initialize your own RoPE
class and pass that instead.
Args:
d_model (int): The dimensionality of the Transformer block input.
num_heads (int): Number of heads to use in multi-headed attention. `d_model` must be
evenly divisible by `num_heads`.
d_ff (int): Dimensionality of the feed-forward inner layer.
max_seq_len (int): Maximum sequence length to pre-cache if your implementation does that.
theta (float): RoPE parameter.
weights (dict[str, Tensor]):
State dict of our reference implementation.
The keys of this dictionary are:
- `attn.q_proj.weight`
The query projections for all `num_heads` attention heads.
Shape is (d_model, d_model).
The rows are ordered by matrices of shape (num_heads, d_k),
so `attn.q_proj.weight == torch.cat([q_heads.0.weight, ..., q_heads.N.weight], dim=0)`.
- `attn.k_proj.weight`
The key projections for all `num_heads` attention heads.
Shape is (d_model, d_model).
The rows are ordered by matrices of shape (num_heads, d_k),
so `attn.k_proj.weight == torch.cat([k_heads.0.weight, ..., k_heads.N.weight], dim=0)`.
- `attn.v_proj.weight`
The value projections for all `num_heads` attention heads.
Shape is (d_model, d_model).
The rows are ordered by matrices of shape (num_heads, d_v),
so `attn.v_proj.weight == torch.cat([v_heads.0.weight, ..., v_heads.N.weight], dim=0)`.
- `attn.output_proj.weight`
Weight of the multi-head self-attention output projection
Shape is (d_model, d_model).
- `ln1.weight`
Weights of affine transform for the first RMSNorm
applied in the transformer block.
Shape is (d_model,).
- `ffn.w1.weight`
Weight of the first linear transformation in the FFN.
Shape is (d_model, d_ff).
- `ffn.w2.weight`
Weight of the second linear transformation in the FFN.
Shape is (d_ff, d_model).
- `ffn.w3.weight`
Weight of the third linear transformation in the FFN.
Shape is (d_model, d_ff).
- `ln2.weight`
Weights of affine transform for the second RMSNorm
applied in the transformer block.
Shape is (d_model,).
in_features (Float[Tensor, "batch sequence_length d_model"]):
Tensor to run your implementation on.
Returns:
Float[Tensor, "batch sequence_length d_model"] Tensor with the output of
running the Transformer block on the input features while using RoPE.
"""
# raise NotImplementedError
transformer_block = transformer.transformer_block(d_model=d_model, num_heads=num_heads, d_ff=d_ff, max_seq_len=max_seq_len, theta=theta)
transformer_block.norm1.weights.data = weights['ln1.weight']
transformer_block.norm2.weights.data = weights['ln2.weight']
transformer_block.attn.q_proj.weight.data = weights['attn.q_proj.weight']
transformer_block.attn.k_proj.weight.data = weights['attn.k_proj.weight']
transformer_block.attn.v_proj.weight.data = weights['attn.v_proj.weight']
transformer_block.attn.output_proj.weight.data = weights['attn.output_proj.weight']
transformer_block.ffn.w1_weight.data = weights['ffn.w1.weight']
transformer_block.ffn.w2_weight.data = weights['ffn.w2.weight']
transformer_block.ffn.w3_weight.data = weights['ffn.w3.weight']
return transformer_block(in_features)运行测试uv run pytest -k test_transformer_block, 结果如下:
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_transformer_block
========================================================================================== test session starts ==========================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 47 deselected / 1 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_transformer_block PASSED
=========================================================================================== warnings summary ============================================================================================
tests/adapters.py:352
/home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics/tests/adapters.py:352: SyntaxWarning: invalid escape sequence '\T'
rope_theta (float): The RoPE $\Theta$ parameter.
-- Docs: https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/how-to/capture-warnings.html
============================================================================== 1 passed, 47 deselected, 1 warning in 0.44s ==============================================================================
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ 警告可以忽略, 这应该是课程组在写注释的时候写了LaTeX风格的字符导致解析出问题
完整的Transformer#
和上面一样, 中间的若干个Transformer Block Layer用nn.ModuleList`来实现
# transformer.py
class transformer_lm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,d_model,num_heads,d_ff,vocab_size,context_length,num_layers,use_rope,max_seq_len=1024,theta=10000):
super().__init__()
self.d_model = d_model
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.d_ff = d_ff
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
self.context_length = context_length
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.max_seq_len = max_seq_len
self.theta = theta
self.Token_Embedding = Embedding(num_embeddings=self.vocab_size, embedding_dim = self.d_model)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([transformer_block(d_model=self.d_model, num_heads=self.num_heads, d_ff=self.d_ff, use_rope=use_rope,max_seq_len=self.max_seq_len, theta=self.theta) for _ in range(self.num_layers)])
self.norm = rmsnorm(d_model = self.d_model)
self.linear = Linear(in_features=self.d_model, out_features=self.vocab_size)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.Token_Embedding(x)
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.linear(x)
# softmax_layer = Softmax(x, dimension=-1)
# return softmax_layer.forward()
return x完善测试接口:
# adapters.py
def run_transformer_lm(
vocab_size: int,
context_length: int,
d_model: int,
num_layers: int,
num_heads: int,
d_ff: int,
rope_theta: float,
weights: dict[str, Tensor],
in_indices: Int[Tensor, " batch_size sequence_length"],
) -> Float[Tensor, " batch_size sequence_length vocab_size"]:
"""Given the weights of a Transformer language model and input indices,
return the output of running a forward pass on the input indices.
This function should use RoPE.
Args:
vocab_size (int): The number of unique items in the output vocabulary to be predicted.
context_length (int): The maximum number of tokens to process at once.
d_model (int): The dimensionality of the model embeddings and sublayer outputs.
num_layers (int): The number of Transformer layers to use.
num_heads (int): Number of heads to use in multi-headed attention. `d_model` must be
evenly divisible by `num_heads`.
d_ff (int): Dimensionality of the feed-forward inner layer (section 3.3).
rope_theta (float): The RoPE $\Theta$ parameter.
weights (dict[str, Tensor]):
State dict of our reference implementation. {num_layers} refers to an
integer between `0` and `num_layers - 1` (the layer index).
The keys of this dictionary are:
- `token_embeddings.weight`
Token embedding matrix. Shape is (vocab_size, d_model).
- `layers.{num_layers}.attn.q_proj.weight`
The query projections for all `num_heads` attention heads.
Shape is (num_heads * (d_model / num_heads), d_model).
The rows are ordered by matrices of shape (num_heads, d_k),
so `attn.q_proj.weight == torch.cat([q_heads.0.weight, ..., q_heads.N.weight], dim=0)`.
- `layers.{num_layers}.attn.k_proj.weight`
The key projections for all `num_heads` attention heads.
Shape is (num_heads * (d_model / num_heads), d_model).
The rows are ordered by matrices of shape (num_heads, d_k),
so `attn.k_proj.weight == torch.cat([k_heads.0.weight, ..., k_heads.N.weight], dim=0)`.
- `layers.{num_layers}.attn.v_proj.weight`
The value projections for all `num_heads` attention heads.
Shape is (num_heads * (d_model / num_heads), d_model).
The rows are ordered by matrices of shape (num_heads, d_v),
so `attn.v_proj.weight == torch.cat([v_heads.0.weight, ..., v_heads.N.weight], dim=0)`.
- `layers.{num_layers}.attn.output_proj.weight`
Weight of the multi-head self-attention output projection
Shape is ((d_model / num_heads) * num_heads, d_model).
- `layers.{num_layers}.ln1.weight`
Weights of affine transform for the first RMSNorm
applied in the transformer block.
Shape is (d_model,).
- `layers.{num_layers}.ffn.w1.weight`
Weight of the first linear transformation in the FFN.
Shape is (d_model, d_ff).
- `layers.{num_layers}.ffn.w2.weight`
Weight of the second linear transformation in the FFN.
Shape is (d_ff, d_model).
- `layers.{num_layers}.ffn.w3.weight`
Weight of the third linear transformation in the FFN.
Shape is (d_model, d_ff).
- `layers.{num_layers}.ln2.weight`
Weights of affine transform for the second RMSNorm
applied in the transformer block.
Shape is (d_model,).
- `ln_final.weight`
Weights of affine transform for RMSNorm applied to the output of the final transformer block.
Shape is (d_model, ).
- `lm_head.weight`
Weights of the language model output embedding.
Shape is (vocab_size, d_model).
in_indices (Int[Tensor, "batch_size sequence_length"]) Tensor with input indices to run the language model on. Shape is (batch_size, sequence_length), where
`sequence_length` is at most `context_length`.
Returns:
Float[Tensor, "batch_size sequence_length vocab_size"]: Tensor with the predicted unnormalized
next-word distribution for each token.
"""
transformerlm = transformer.transformer_lm(d_model=d_model,num_heads=num_heads,d_ff=d_ff,vocab_size=vocab_size,
context_length=context_length,num_layers=num_layers,use_rope=True,theta=rope_theta)
transformerlm.Token_Embedding.weight.data = weights['token_embeddings.weight']
for layer_idx in range(num_layers):
block = transformerlm.layers[layer_idx]
# Attention weights
block.attn.q_proj.weight.data = weights[f'layers.{layer_idx}.attn.q_proj.weight']
block.attn.k_proj.weight.data = weights[f'layers.{layer_idx}.attn.k_proj.weight']
block.attn.v_proj.weight.data = weights[f'layers.{layer_idx}.attn.v_proj.weight']
block.attn.output_proj.weight.data = weights[f'layers.{layer_idx}.attn.output_proj.weight']
# RMSNorm weights
block.norm1.weights.data = weights[f'layers.{layer_idx}.ln1.weight']
block.norm2.weights.data = weights[f'layers.{layer_idx}.ln2.weight']
# FFN weights
block.ffn.w1_weight.data = weights[f'layers.{layer_idx}.ffn.w1.weight']
block.ffn.w2_weight.data = weights[f'layers.{layer_idx}.ffn.w2.weight']
block.ffn.w3_weight.data = weights[f'layers.{layer_idx}.ffn.w3.weight']
transformerlm.norm.weights.data = weights['ln_final.weight']
transformerlm.linear.weight.data = weights['lm_head.weight']
return transformerlm(in_indices)
# raise NotImplementedError运行测试uv run pytest -k test_transformer_lm, 结果如下:
(base) zyli@lab:~/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics$ uv run pytest -k test_transformer_lm
========================================================================================== test session starts ==========================================================================================
platform linux -- Python 3.13.5, pytest-8.4.1, pluggy-1.6.0
rootdir: /home/zyli/Stanford_CS336/assignment1-basics
configfile: pyproject.toml
plugins: jaxtyping-0.3.2
collected 48 items / 46 deselected / 2 selected
tests/test_model.py::test_transformer_lm PASSED
tests/test_model.py::test_transformer_lm_truncated_input PASSED
=================================================================================== 2 passed, 46 deselected in 0.46s ====================================================================================计算次数估算#
模型训练的时候, 绝大部分运算都是矩阵乘法里面的数值乘法运算, 注意以下事实: 如果, , 那么的计算次数是
参数数量计算和内存用量#
考虑第一个问题, 对于以下配置的, 有多少个可训练的参数? 如果每个参数都是单精度浮点数, 那么读取这个模型需要多少内存?
vocab_size = 50257
context_length = 1024
num_layers = 48
d_model = 1600
nun_heads = 25
d_ff = 6400对于Embedding Layer, 有个参数
50257 * 1600 = 80,411,200对于一个Transformer Block, 有两个RMSNorm, 每个RMSNorm有个参数, 有一个multihead_self_attention, 其中有四个矩阵, 参数量总共为, 对于positionwise_feedforward, 有两个矩阵, 总参数量为
2 * 1600 + 4 * 1600 * 1600 + 2 * 1600 * 6400 = 3200 + 10240000 + 20480000 = 30,723,200除此之外, 输出前还有一个RMSNorm,一个Linear, 总参数量为
1600 + 1600 * 50257 = 80,412,800故总共有
80411200 + 30723200 * 48 + 80412800 = 1,635,537,600大概1.6B的参数量
1,635,537,600 * 4 /1024 /1024 /1024 = 6.1GB需要内存约6.1GB
FLOPS次数估计#
如果这个模型前向传播一次, 需要多少次FLOPS?
在一个transformer_block中, 一次multihead_self_attention的计算次数由以下部分组成:
Q投影: 2 * seq_len * d_model * d_model
K投影: 2 * seq_len * d_model * d_model
V投影: 2 * seq_len * d_model * d_model
输出投影: 2 * seq_len * d_model * d_model
QK^T: 2 * seq_len * seq_len * d_model
Attn V: 2 * seq_len * seq_len * d_model
共计8 * seq_len * d_model² + 4 * seq_len² * d_model = 20,971,520,000 + 67,108,864,000 = 88,080,384,000一次positionwise_feedforward的计算次数由以下部分组成:
w_1x: 2 * seq_len * d_model * d_ff
W_3x: 2 * seq_len * d_model * d_ff
W2 @ (SiLU(W1x) ⊙ W3x): 2 * seq_len * d_model * d_ff
共计6 * seq_len * d_model * d_ff = 62,914,560,000输出前有一个Output_Embedding的线性层, 计算次数为
2 * seq_len * d_model * vocab_size = 164,682,137,600代入配置, 得到
48 * (88,080,384,000 + 62,914,560,000) + 164,682,137,600 = 7,412,439,449,600大约7.4TeraFLOPs